
What Is a 51% Attack and How Does It Work
A 51% attack is an attack on a cryptocurrency when а miner or group of miners successfully hijacks and controls more than 50% of a blockchain's hash rate. By having over 50% control of the blockchain hash rate, rogue attackers can manipulate cryptocurrency transaction records on the blockchain.
The difficulty of executing a 51% attack on a cryptocurrency depends on the network's cumulative hash rate. Namely, it's much more challenging for an attacker to execute a 51% attack on a blockchain with a very high hash rate. And vice versa, executing the attack on networks with a lower hash rate is proportionally easier.
*Note: The hash rate is the total computational power used by miners in Proof-of-Work blockchains to process transactions.
When an attacker or group of attackers controls over half of the total computational power in a Proof-of-Work blockchain, they can manipulate transactions and double-spend coins without anyone else in the network being able to do anything about it.
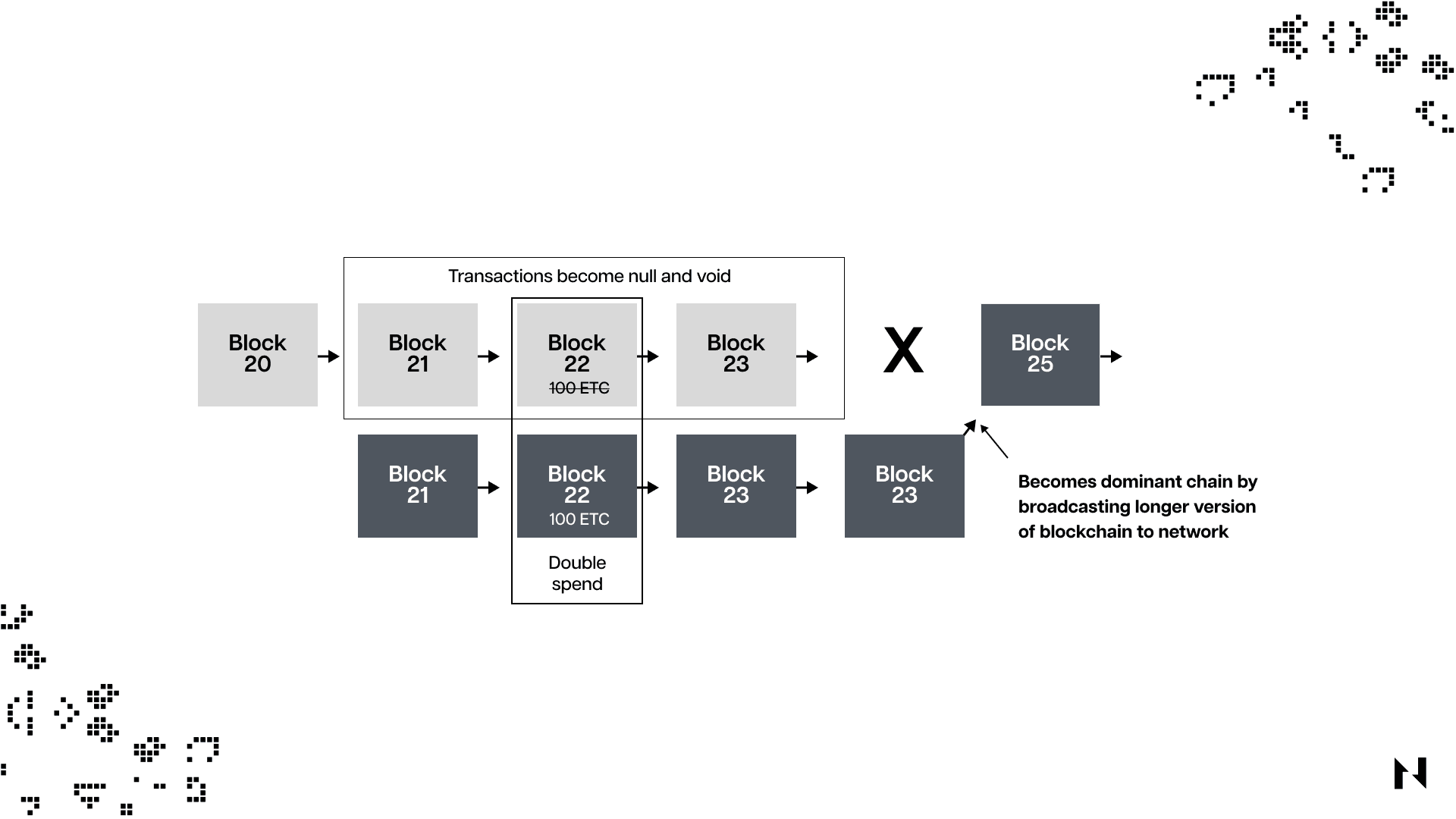
When nobody controls over half of the hash rate, nobody can alter the transaction and expect the majority will accept it. But if the attackers hold most of the blockchain's hash rate, the honest nodes will have no power to stop it, even if they all suspect it.
It's essential to recognize that a 51% attack on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain is not the same as a 51% attack on a Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchain. With Proof-of-Stake blockchains, the attackers would have to own over half of the staked cryptocurrencies on the blockchain and not the majority of the hash rate.
A blockchain like Bitcoin is secure when nobody controls over half its hash rate, while a Proof-of-Stake blockchain like Ethereum is secure when nobody controls over half of its staked cryptocurrencies.
Why Are 51% Attack Risks Important to Miners?
Understanding the potential risks associated with 51% attacks is a crucial aspect for miners, given the considerable investment in computational resources and electricity costs they bear. The occurrence of such an attack can compromise the blockchain, rendering it unprofitable for honest miners to participate in mining activities and subsequently impacting the underlying cryptocurrency's price. Therefore, it is imperative for miners to mine Proof-of-Work blockchains that are not susceptible to 51% attacks and have long-term security assurances.
What Happens When an Attacker Gains Control of 51% of a Network’s Hash Rate?
An attacker controlling over half of a Proof-of-Work blockchain hash rate can easily manipulate cryptocurrency transactions. These transaction manipulations can severely impact the targeted cryptocurrency’s price and credibility.
The attackers could enforce their version of manipulated transaction validations since they control over half of the hash rate, and they can reverse recently confirmed transactions to spend the same cryptocurrencies twice. This strategy is called double-spending. Attackers do this to keep spending the same amount of coins multiple times.
Not only double-spending problems but 51% attacks also enable the attackers to make a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack, where the attackers can filter out the addresses of other miners or validators before the compromised chain eventually becomes permanent.
Imagine a scenario where everybody in a store can buy 20 shirts with the same $10 bill. The store will go bankrupt because everybody will abuse it. This will also happen when a blockchain gets abused by 51% of attackers.
The attackers will keep re-spending the same cryptocurrencies and dump them for other cryptocurrencies as fast as possible, and move them to fiat through some shady cryptocurrency money laundering practices.
How Does the Hash Rate of a Blockchain Network Affect Its Security and Performance?
Speaking about blockchain hash rate and security, everything depends on factors like mining difficulty, blockchain adoption, the blockchain’s cryptocurrency price, and how many miners are competing in the same blockchain.
When there is more adoption for a specific blockchain, it’s more likely for the blockchain’s cryptocurrency price to go up. Thus, more miners will enter the same network since they can make money. And when more miners have more advanced mining computers in the same Proof-of-Work blockchain, mining difficulty increases, and the blockchain hash rate increases.
Blockchain networks with higher hash rates are considered more secure because attackers may consider attacks too expensive. For example, an established Proof-of-Work blockchain like Bitcoin has an enormous hash rate, meaning a 51% attack attempt can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars per day to execute successfully. This is why these attacks have historically occurred on smaller blockchains with much weaker hash rates.
Factors that Affect a Blockchain’s Hash Rate
Several factors can affect the hash rate of Proof-of-Work blockchains, including:
- The mining difficulty
- The number of participating miners
- The cumulative power of the miners’ mining rigs
- The profitability of the mining rewards
As mentioned before, when there are more miners in the same blockchain network, the mining difficulty should increase, and thus, the blockchain’s hash rate and its overall security will increase.
Can Blockchains Defend Against 51% Attacks?
51% attacks pose a significant threat to the security and reliability of blockchain networks, which is why they must maintain a sufficient hash rate and decentralization, as this significantly increases the difficulty and cost for potential attackers.
In the case of well-established networks like Bitcoin, the likelihood of a 51% attack occurring is minimal, especially when considering their extremely high hash and decentralization. However, smaller blockchain networks are more vulnerable to such attacks, and attackers with substantial resources may attempt to compromise them when opportunities arise.
To protect against 51% attacks, smaller blockchain networks should increase their adoption, as this would increase both decentralization and hash rate. Additionally, it is essential to note that different Proof-of-Work algorithms employed by various blockchains can help mitigate the risks associated with 51% attacks.

